1D-CNNでSpeaker Recognition
1D-CNNを使って、音声データから発話者の識別を行います。
下のデータセットを使います。
Speaker Recognition Dataset|Kaggle Dataset
作成のきっかけKerasのSpeaker Recognitionです。こちらは、FFT(高速フーリエ変換)をしていますが、ここでは変換なしで行います。(Normalizeすらしてなかったので、後でします。)
PyTorchのコード
import time import os import glob from pathlib import Path import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import librosa import librosa.display %matplotlib inline import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
ラベル
speaker_label = {'Jens_Stoltenberg' : 0,
'Benjamin_Netanyau': 1,
'Julia_Gillard' : 2,
'Magaret_Tarcher' : 3,
'Nelson_Mandela' : 4,
}
データの読み込み
def Read_file_label(path_name, speaker_label):
file_label_list = []
file_list = []
label_list = []
for label in speaker_label.keys():
n_file = len(glob.glob(os.path.join(path_name, list(speaker_label.keys())[0])+"/*.wav"))
for i in range(n_file):
file_label_list.append((os.path.join(path_name, label, f"{i}.wav"), speaker_label[label]))
file_list.append(os.path.join(path_name, label, f"{i}.wav"))
label_list.append(speaker_label[label])
return file_label_list, file_list, label_list
class Audio_Datasets(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, file_label_list, sr):
self.path = file_label_list
self.sr = sr
def __len__(self):
return len(self.path)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
data, _ = librosa.load(self.path[idx][0], sr=self.sr)
#data = data[:self.sr]
data = data.reshape(1, self.sr)
label = np.array(self.path[idx][1])
return data, label
file_label_list, file_list, label_list = Read_file_label(path_name, speaker_label)
X_train, X_valid, y_train, y_valid = train_test_split(file_list, label_list, test_size=0.2, random_state=31)
train = [(X_train[idx], y_train[idx]) for idx in range(len(X_train))]
valid = [(X_valid[idx], y_valid[idx]) for idx in range(len(X_valid))]
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(Audio_Datasets(train, sr), batch_size=128, shuffle = True)
valid_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(Audio_Datasets(valid, sr), batch_size=128, shuffle = True)
ネットワーク
ネットワークの構成は適当なので、参考程度に…
後で、しっかりしたものにしたい…
class Net1D(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net1D,self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv1d(1, 8, kernel_size=3, stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm1d(8),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv1d(8, 32, kernel_size=5, stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm1d(32),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=5, stride=2),
)
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv1d(32, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm1d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=7, stride=2),
)
self.conv4 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv1d(64, 128, kernel_size=9, stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm1d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=9, stride=2),
)
self.dense = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(126464, 512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(512,128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(128, 5),
)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.conv4(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0),-1)
x = self.dense(x)
return x
def check_size(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.conv4(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0),-1)
return x
LossとAccuracy
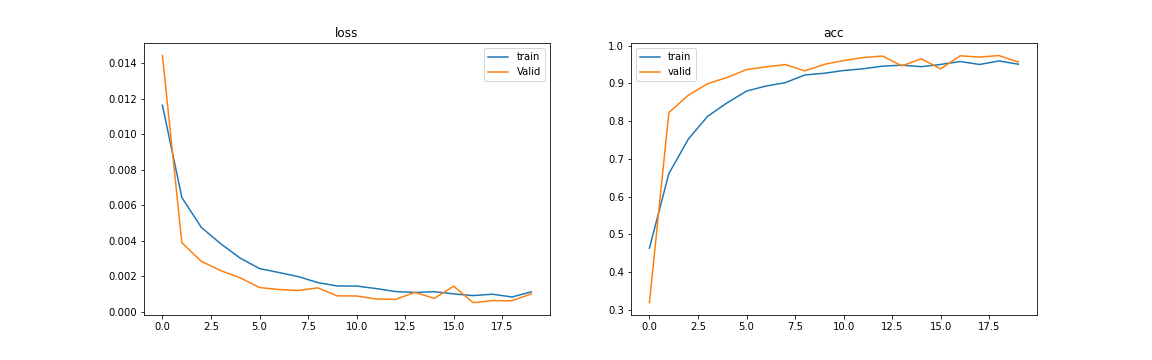
コード全体
GitHub - betashort/Speaker_Recognition
...
参考

Keras documentation: Speaker Recognition
...
Just a moment...